August 1, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL BETWEEN operator to match a value against a range of values.
Table of Contents
Introduction to the PostgreSQL BETWEEN operator
You use the BETWEEN operator to match a value against a range of values. The following illustrates the syntax of the BETWEEN operator:
value BETWEEN low AND high;
If the value is greater than or equal to the low value and less than or equal to the high value, the expression returns true, otherwise, it returns false.
You can rewrite the BETWEEN operator by using the greater than or equal ( >=) or less than or equal ( <=) operators like this:
value >= low and value <= high
If you want to check if a value is out of a range, you combine the NOT operator with the BETWEEN operator as follows:
value NOT BETWEEN low AND high;
The following expression is equivalent to the expression that uses the NOT and BETWEEN operators:
value < low OR value > high
You often use the BETWEEN operator in the WHERE clause of a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE statement.
PostgreSQL BETWEEN operator examples
Let’s take a look at the payment table in the sample database.

The following query use the BETWEEN operator to select payments whose amount is between 8 and 9 (USD):
SELECT
customer_id,
payment_id,
amount
FROM
payment
WHERE
amount BETWEEN 8 AND 9;

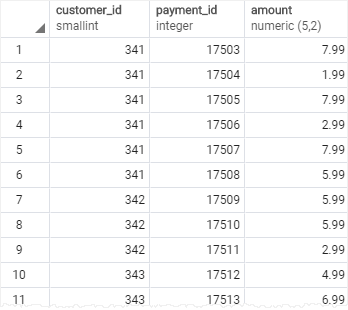
To get payments whose amount is not in the range of 8 and 9, you use the following query:
SELECT
customer_id,
payment_id,
amount
FROM
payment
WHERE
amount NOT BETWEEN 8 AND 9;
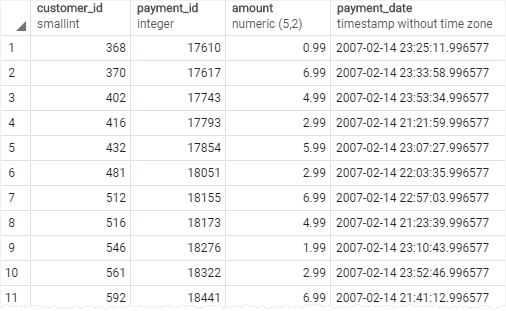
If you want to check a value against of date ranges, you should use the literal date in ISO 8601 format i.e., YYYY-MM-DD. For example, to get the payment whose payment date is between 2007-02-07 and 2007-02-15, you use the following query:
SELECT
customer_id,
payment_id,
amount,
payment_date
FROM
payment
WHERE
payment_date BETWEEN '2007-02-07' AND '2007-02-15';
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use PostgreSQL BETWEEN operator to select a value that is in a range of values.

