August 1, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL UPDATE statement to update existing data in a table.
Table of Contents
Introduction to the PostgreSQL UPDATE statement
The PostgreSQL UPDATE statement allows you to modify data in a table. The following illustrates the syntax of the UPDATE statement:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1,
column2 = value2,
...
WHERE condition;
In this syntax:
- First, specify the name of the table that you want to update data after the
UPDATEkeyword. - Second, specify columns and their new values after
SETkeyword. The columns that do not appear in theSETclause retain their original values. - Third, determine which rows to update in the condition of the WHERE clause.
The WHERE clause is optional. If you omit the WHERE clause, the UPDATE statement will update all rows in the table.
When the UPDATE statement is executed successfully, it returns the following command tag:
UPDATE count
The count is the number of rows updated including rows whose values did not change.
Returning updated rows
The UPDATE statement has an optional RETURNING clause that returns the updated rows:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1,
column2 = value2,
...
WHERE condition
RETURNING * | output_expression AS output_name;
PostgreSQL UPDATE examples
Let’s take some examples of using the PostgreSQL UPDATE statement.
Setting up a sample table
The following statements create a table called courses and insert some data into it:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS courses;
CREATE TABLE courses(
course_id serial primary key,
course_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description VARCHAR(500),
published_date date
);
INSERT INTO
courses(course_name, description, published_date)
VALUES
('PostgreSQL for Developers','A complete PostgreSQL for Developers','2020-07-13'),
('PostgreSQL Admininstration','A PostgreSQL Guide for DBA',NULL),
('PostgreSQL High Performance',NULL,NULL),
('PostgreSQL Bootcamp','Learn PostgreSQL via Bootcamp','2013-07-11'),
('Mastering PostgreSQL','Mastering PostgreSQL in 21 Days','2012-06-30');
The following statement returns the data from the courses table:
SELECT * FROM courses;

1) PostgreSQL UPDATE – updating one row
The following statement uses the UPDATE statement to update the course with id 3. It changes the published_date from NULL to '2020-08-01'.
UPDATE courses
SET published_date = '2020-08-01'
WHERE course_id = 3;
The statement returns the following message indicating that one row has been updated:
UPDATE 1
The following statement selects the course with id 3 to verify the update:
SELECT * FROM courses
WHERE course_id = 3;

2) PostgreSQL UPDATE – updating a row and returning the updated row
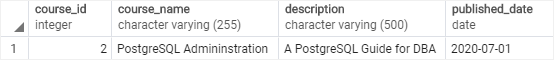
The following statement updates course id 2. It modifies published_date of the course to 2020-07-01 and returns the updated course.
UPDATE courses
SET published_date = '2020-07-01'
WHERE course_id = 2
RETURNING *;
Summary
- Use the PostgreSQL
UPDATEstatement to update data in one or more columns of a table. - Use the
RETURNINGclause to return the updated rows from theUPDATEstatement

