August 1, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL INSERT statement to insert a new row into a table.
Table of Contents
Introduction to PostgreSQL INSERT statement
The PostgreSQL INSERT statement allows you to insert a new row into a table.
The following illustrates the most basic syntax of the INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO table_name(column1, column2, …)
VALUES (value1, value2, …);
In this syntax:
-
First, specify the name of the table (
table_name) that you want to insert data after theINSERT INTOkeywords and a list of comma-separated columns (colum1, column2, ....). -
Second, supply a list of comma-separated values in a parentheses
(value1, value2, ...)after theVALUESkeyword. The columns and values in the column and value lists must be in the same order.
The INSERT statement returns a command tag with the following form:
INSERT oid count
OID is an object identifier. PostgreSQL used the OID internally as a primary key for its system tables. Typically, the INSERT statement returns OID with value 0. The count is the number of rows that the INSERT statement inserted successfully.
RETURNING clause
The INSERT statement also has an optional RETURNING clause that returns the information of the inserted row.
If you want to return the entire inserted row, you use an asterisk (*) after the RETURNING keyword:
INSERT INTO table_name(column1, column2, …)
VALUES (value1, value2, …)
RETURNING *;
If you want to return just some information of the inserted row, you can specify one or more columns after the RETURNING clause.
For example, the following statement returns the id of the inserted row:
INSERT INTO table_name(column1, column2, …)
VALUES (value1, value2, …)
RETURNING id;
To rename the returned value, you use the AS keyword followed by the name of the output. For example:
INSERT INTO table_name(column1, column2, …)
VALUES (value1, value2, …)
RETURNING output_expression AS output_name;
PostgreSQL INSERT statement examples
The following statement creates a new table calledlinksfor the demonstration:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS links;
CREATE TABLE links (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
url VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description VARCHAR (255),
last_update DATE
);
Note that you will learn how to create a new table in the subsequent tutorial. In this tutorial, you just need to execute it to create a new table.
1) PostgreSQL INSERT – Inserting a single row into a table
The following statement inserts a new row into the links table:
INSERT INTO links (url, name)
VALUES('https://www.rockdata.net/tutorial/','PostgreSQL Tutorial');
The statement returns the following output:
INSERT 0 1
To insert character data, you enclose it in single quotes (‘) for example 'PostgreSQL Tutorial'.
If you omit required columns in the INSERT statement, PostgreSQL will issue an error. In case you omit an optional column, PostgreSQL will use the column default value for insert.
In this example, the description is an optional column because it doesn’t have a NOT NULL constraint. Therefore, PostgreSQL uses NULL to insert into the description column.
PostgreSQL automatically generates a sequential number for the serial column so you do not have to supply a value for the serial column in the INSERT statement.
The following SELECT statement shows the contents of the links table:
SELECT * FROM links;

2) PostgreSQL INSERT – Inserting character string that contains a single quote
If you want to insert a string that contains a single quote (') such as O'Reilly Media, you have to use an additional single quote (') to escape it. For example:
INSERT INTO links (url, name)
VALUES('http://www.oreilly.com','O''Reilly Media');
Output:
INSERT 0 1
The following statement verifies the insert:
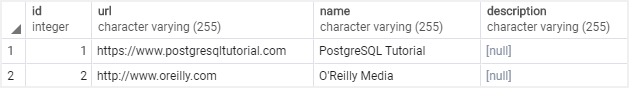
3) PostgreSQL INSERT – Inserting a date value
To insert a date value into a column with the DATE type, you use the date in the format 'YYYY-MM-DD'.
The following statement inserts a new row with a specified date into the links table:
INSERT INTO links (url, name, last_update)
VALUES('https://www.google.com','Google','2013-06-01');
Output:
INSERT 0 1
4) PostgreSQL INSERT- Getting the last insert id
To get the last insert id from inserted row, you use the RETURNING clause of the INSERTstatement.
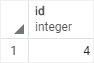
For example, the following statement inserts a new row into the links table and returns the last insert id:
INSERT INTO links (url, name)
VALUES('http://www.postgresql.org','PostgreSQL')
RETURNING id;
Output:
Summary
- Use PostgreSQL
INSERTstatement to insert data into a table. - Use the
RETURNINGclause to get the inserted rows.

