September 15, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use various techniques to delete duplicate rows in PostgreSQL.
Preparing sample data
First, create a new table named basket that stores fruits:
CREATE TABLE basket(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
fruit VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
);
Second, insert some fruits into the basket table.
INSERT INTO basket(fruit) values('apple');
INSERT INTO basket(fruit) values('apple');
INSERT INTO basket(fruit) values('orange');
INSERT INTO basket(fruit) values('orange');
INSERT INTO basket(fruit) values('orange');
INSERT INTO basket(fruit) values('banana');
Third, query data from the basket table:
SELECT
id,
fruit
FROM
basket;

As you can see, we have some duplicate rows such as 2 apples and 3 oranges in the basket table.
Finding duplicate rows
If the table has few rows, you can see which ones are duplicate immediately. However, it is not the case with the big table.
The find the duplicate rows, you use the following statement:
SELECT
fruit,
COUNT( fruit )
FROM
basket
GROUP BY
fruit
HAVING
COUNT( fruit )> 1
ORDER BY
fruit;

Deleting duplicate rows using DELETE USING statement
The following statement uses the DELETE USING statement to remove duplicate rows:
DELETE FROM
basket a
USING basket b
WHERE
a.id < b.id
AND a.fruit = b.fruit;
In this example, we joined the basket table to itself and checked if two different rows (a.id < b.id) have the same value in the fruit column.
Let’s query the basket table again to verify whether the duplicate rows were deleted:
SELECT
id,
fruit
FROM
basket;
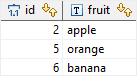
As you can see, the statement removed the duplicate rows with lowest ids and keep the one with the highest id.
If you want to keep the duplicate rows with the lowest id, you use just need to flip the operator in the WHERE clause:
DELETE FROM
basket a
USING basket b
WHERE
a.id > b.id
AND a.fruit = b.fruit;
To check whether the statement works correctly, let’s verify the data in the basket table:
SELECT
id,
fruit
FROM
basket;
Result:
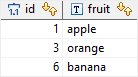
Perfect! the duplicate rows with the lowest ids are retained.
Deleting duplicate rows using subquery
The following statement uses a suquery to delete duplicate rows and keep the row with the lowest id.
DELETE FROM basket
WHERE id IN
(SELECT id
FROM
(SELECT id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER( PARTITION BY fruit
ORDER BY id ) AS row_num
FROM basket ) t
WHERE t.row_num > 1 );
In this example, the subquery returned the duplicate rows except for the first row in the duplicate group. And the outer DELETE statement deleted the duplicate rows returned by the subquery.
If you want to keep the duplicate row with highest id, just change the order in the subquery:
DELETE FROM basket
WHERE id IN
(SELECT id
FROM
(SELECT id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER( PARTITION BY fruit
ORDER BY id DESC ) AS row_num
FROM basket ) t
WHERE t.row_num > 1 );
In case you want to delete duplicate based on values of multiple columns, here is the query template:
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE id IN
(SELECT id
FROM
(SELECT id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER( PARTITION BY column_1,
column_2
ORDER BY id ) AS row_num
FROM table_name ) t
WHERE t.row_num > 1 );
In this case, the statement will delete all rows with duplicate values in the column_1 and column_2 columns.
Deleting duplicate rows using an immediate table
To delete rows using an immediate table, you use the following steps:
- Create a new table with the same structure as the one whose duplicate rows should be removed.
- Insert distinct rows from the source table to the immediate table.
- Drop the source table.
- Rename the immediate table to the name of the source table.
The following illustrates the steps of removing duplicate rows from the basket table:
-- step 1
CREATE TABLE basket_temp (LIKE basket);
-- step 2
INSERT INTO basket_temp(fruit, id)
SELECT
DISTINCT ON (fruit) fruit,
id
FROM basket;
-- step 3
DROP TABLE basket;
-- step 4
ALTER TABLE basket_temp
RENAME TO basket;
In this tutorial, you have learned how to delete duplicate rows in PostgreSQL using the DELETE USING statement, subquery, and the immediate table techniques.

