August 1, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL UPDATE join syntax to update data in a table based on values in another table.
Table of Contents
Introduction to the PostgreSQL UPDATE join syntax
Sometimes, you need to update data in a table based on values in another table. In this case, you can use the PostgreSQL UPDATE join syntax as follows:
UPDATE t1
SET t1.c1 = new_value
FROM t2
WHERE t1.c2 = t2.c2;
To join to another table in the UPDATE statement, you specify the joined table in the FROM clause and provide the join condition in the WHERE clause. The FROM clause must appear immediately after the SET clause.
For each row of table t1, the UPDATE statement examines every row of table t2. If the value in the c2 column of table t1 equals the value in the c2 column of table t2, the UPDATE statement updates the value in the c1 column of the table t1 the new value (new_value).
PostgreSQL UPDATE JOIN example
Let’s take a look at an example to understand how the PostgreSQL UPDATE join works. We will use the following database tables for the demonstration:
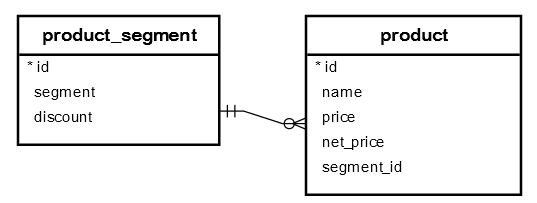
First, create a new table called product_segment that stores the product segments including grand luxury, luxury, and mass.
The product_segment table has the discount column that stores the discount percentage based on a specific segment. For example, products with the grand luxury segment have 5% discount while luxury and mass products have 6% and 10% discounts respectively.
CREATE TABLE product_segment (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
segment VARCHAR NOT NULL,
discount NUMERIC (4, 2)
);
INSERT INTO
product_segment (segment, discount)
VALUES
('Grand Luxury', 0.05),
('Luxury', 0.06),
('Mass', 0.1);
Second, create another table named product that stores the product data. The product table has the foreign key column segment_id that links to the id of the segment table.
CREATE TABLE product(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
price NUMERIC(10,2),
net_price NUMERIC(10,2),
segment_id INT NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY(segment_id) REFERENCES product_segment(id)
);
INSERT INTO
product (name, price, segment_id)
VALUES
('diam', 804.89, 1),
('vestibulum aliquet', 228.55, 3),
('lacinia erat', 366.45, 2),
('scelerisque quam turpis', 145.33, 3),
('justo lacinia', 551.77, 2),
('ultrices mattis odio', 261.58, 3),
('hendrerit', 519.62, 2),
('in hac habitasse', 843.31, 1),
('orci eget orci', 254.18, 3),
('pellentesque', 427.78, 2),
('sit amet nunc', 936.29, 1),
('sed vestibulum', 910.34, 1),
('turpis eget', 208.33, 3),
('cursus vestibulum', 985.45, 1),
('orci nullam', 841.26, 1),
('est quam pharetra', 896.38, 1),
('posuere', 575.74, 2),
('ligula', 530.64, 2),
('convallis', 892.43, 1),
('nulla elit ac', 161.71, 3);
Third, suppose you have to calculate the net price of every product based on the discount of the product segment. To do this, you can apply the UPDATE join statement as follows:
UPDATE product
SET net_price = price - price * discount
FROM product_segment
WHERE product.segment_id = product_segment.id;
You can utilize the table aliases to make the query shorter like this:
UPDATE
product p
SET
net_price = price - price * discount
FROM
product_segment s
WHERE
p.segment_id = s.id;
This statement joins the product table to the product_segment table. If there is a match in both tables, it gets the discount from the product_segment table, calculates the net price based on the following formula, and updates the net_price column.
net_price = price - price * discount;
The following SELECT statement retrieves the data of the product table to verify the update:
SELECT * FROM product;

As you can see, the net_price column has been updated with the correct values.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL UPDATE join statement to update data in a table based on values in another table.

