August 2, 2023
Summary: In this tutorial, you will learn how to leverage the indexes on expression to improve the performance of queries that involve expressions.
Table of Contents
Introduction to PostgreSQL index on expression
Normally, you create an index that references one or more columns of a table. But you can also create an index based on an expression that involves table columns. This index is called an index on expression.
The indexes on expressions are also known as functional-based indexes.
The syntax for creating an index on expression is as follows:
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (expression);
In this statement:
- First, specify the name of the index after the
CREATE INDEXclause. - Then, form an expression that involves table columns of the
table_name.
Once you define an index expression, PostgreSQL will consider using that index when the expression that defines the index appears in the WHERE clause or in the ORDER BY clause of the SQL statement.
Note that indexes on expressions are quite expensive to maintain because PostgreSQL has to evaluate the expression for each row when it is inserted or updated and use the result for indexing. Therefore, you should use the indexes on expressions when retrieval speed is more critical than insertion and update speed.
PostgreSQL index on expression example
Let’s see the customer table from the sample database.
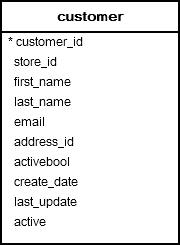
The customer table has a B-Tree index defined for the first_name column. The following query finds customers whose last name is Purdy:
SELECT
customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
FROM
customer
WHERE
last_name = 'Purdy';
When executing this query, PostgreSQL uses the idx_last_name index as shown in the following EXPLAIN statement:
EXPLAIN
SELECT
customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
FROM
customer
WHERE
last_name = 'Purdy';

The following statement finds customers whose last name is purdy in lowercase. However, PostgreSQL could not utilize the index for lookup:
EXPLAIN
SELECT
customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
FROM
customer
WHERE
LOWER(last_name) = 'purdy';
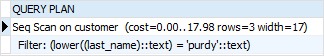
To improve this query, you can define an index expression like this:
CREATE INDEX idx_ic_last_name
ON customer(LOWER(last_name));
Now, the query that finds customers based on the last name in a case-insensitive manner will use the index on expression as shown below:
EXPLAIN
SELECT
customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
FROM
customer
WHERE
LOWER(last_name) = 'purdy';

In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL index on expression to improve queries that have an expression that involves table columns.

