August 1, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you what the primary key is and how to manage PostgreSQL primary key constraints through SQL statements.
A primary key is a column or a group of columns used to identify a row uniquely in a table.
You define primary keys through primary key constraints. Technically, a primary key constraint is the combination of a not-null constraint and a UNIQUE constraint.
A table can have one and only one primary key. It is a good practice to add a primary key to every table. When you add a primary key to a table, PostgreSQL creates a unique B-tree index on the column or a group of columns used to define the primary key.
Define primary key when creating the table
Normally, we add the primary key to a table when we define the table’s structure using CREATE TABLE statement.
CREATE TABLE TABLE (
column_1 data_type PRIMARY KEY,
column_2 data_type,
…
);
The following statement creates a purchase order (PO) header table with the name po_headers.
CREATE TABLE po_headers (
po_no INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
vendor_no INTEGER,
description TEXT,
shipping_address TEXT
);
The po_no is the primary key of the po_headers table, which uniquely identifies purchase order in the po_headers table.
In case the primary key consists of two or more columns, you define the primary key constraint as follows:
CREATE TABLE TABLE (
column_1 data_type,
column_2 data_type,
…
PRIMARY KEY (column_1, column_2)
);
For example, the following statement creates the purchase order line items table whose primary key is a combination of purchase order number ( po_no) and line item number ( item_no).
CREATE TABLE po_items (
po_no INTEGER,
item_no INTEGER,
product_no INTEGER,
qty INTEGER,
net_price NUMERIC,
PRIMARY KEY (po_no, item_no)
);
If you don’t specify explicitly the name for primary key constraint, PostgreSQL will assign a default name to the primary key constraint. By default, PostgreSQL uses table-name_pkey as the default name for the primary key constraint. In this example, PostgreSQL creates the primary key constraint with the name po_items_pkey for the po_items table.
In case you want to specify the name of the primary key constraint, you use CONSTRAINT clause as follows:
CONSTRAINT constraint_name PRIMARY KEY(column_1, column_2,...);
Define primary key when changing the existing table structure
It is rare to define a primary key for existing table. In case you have to do it, you can use the ALTER TABLE statement to add a primary key constraint.
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD PRIMARY KEY (column_1, column_2);
The following statement creates a table named products without defining any primary key.
CREATE TABLE products (
product_no INTEGER,
description TEXT,
product_cost NUMERIC
);
Suppose you want to add a primary key constraint to the products table, you can execute the following statement:
ALTER TABLE products
ADD PRIMARY KEY (product_no);
How to add an auto-incremented primary key to an existing table
Suppose, we have a vendors table that does not have any primary key.
CREATE TABLE vendors (name VARCHAR(255));
And we add few rows to the vendors table using INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO vendors (NAME)
VALUES
('Microsoft'),
('IBM'),
('Apple'),
('Samsung');
To verify the insert operation, we query data from the vendors table using the following SELECT statement:
SELECT * FROM vendors;

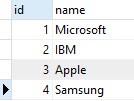
Now, if we want to add a primary key named id into the vendors table and the id field is auto-incremented by one, we use the following statement:
ALTER TABLE vendors ADD COLUMN ID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY;
Let’s check the vendors table again.
SELECT id, name FROM vendors;
Remove primary key
To remove an existing primary key constraint, you also use the ALTER TABLE statement with the following syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP CONSTRAINT primary_key_constraint;
For example, to remove the primary key constraint of the products table, you use the following statement:
ALTER TABLE products
DROP CONSTRAINT products_pkey;
In this tutorial, you have learned how to add and remove primary key constraints using CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements.

