August 2, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to work with PostgreSQL array and introduce you to some handy functions for array manipulation.
Table of Contents
Introduction to the PostgreSQL Array type
Array plays an important role in PostgreSQL. Every data type has its own companion array type e.g., integer has an integer[] array type, character has character[] array type, etc. In case you define your own data type, PostgreSQL creates a corresponding array type in the background for you.
PostgreSQL allows you to define a column to be an array of any valid data type including built-in type, user-defined type or enumerated type.
The following CREATE TABLE statement creates the contacts table with the phones column is defined as an array of text.
CREATE TABLE contacts (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR (100),
phones TEXT []
);
The phones column is a one-dimensional array that holds various phone numbers that a contact may have.
Insert PostgreSQL array values
The following statement inserts a new contact into the contacts table.
INSERT INTO contacts (name, phones)
VALUES('John Doe',ARRAY [ '(408)-589-5846','(408)-589-5555' ]);
We used the ARRAY constructor to construct an array and insert it into the contacts table. You can also use curly braces as follows:
INSERT INTO contacts (name, phones)
VALUES('Lily Bush','{"(408)-589-5841"}'),
('William Gate','{"(408)-589-5842","(408)-589-58423"}');
The statement above inserts two rows into the contacts table. Notice that when you use curly braces, you use single quotes ' to wrap the array and double quotes " to wrap text array items.
Query array data
You use the SELECT statement to query array data as follows:
SELECT
name,
phones
FROM
contacts;
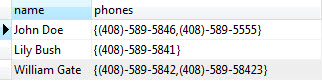
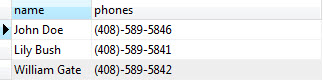
We access array elements using the subscript within square brackets []. By default, PostgreSQL uses one-based numbering for array elements. It means the first array element starts with number 1. Suppose, we want to get the contact’s name and the first phone number, we use the following query:
SELECT
name,
phones [ 1 ]
FROM
contacts;
We can use array element in the WHERE clause as the condition to filter the rows. For example, to find out who has the phone number (408)-589-58423 as the second phone number, we use the following query.
SELECT
name
FROM
contacts
WHERE
phones [ 2 ] = '(408)-589-58423';

Modifying PostgreSQL array
PostgreSQL allows you to update each element of an array or the whole array. The following statement updates the second phone number of William Gate.
UPDATE contacts
SET phones [2] = '(408)-589-5843'
WHERE ID = 3;
Let’s check it again.
SELECT
id,
name,
phones [ 2 ]
FROM
contacts
WHERE
id = 3;
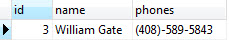
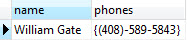
The following statement updates an array as a whole.
UPDATE contacts
SET phones = '{"(408)-589-5843"}'
WHERE id = 3;
We verify the update using the following statement.
SELECT
name,
phones
FROM
contacts
WHERE
id = 3;
Search in PostgreSQL Array
Suppose, we want to know who has the phone number (408)-589-5555 regardless of position of the phone number in the phones array, we use ANY() function as follows:
SELECT
name,
phones
FROM
contacts
WHERE
'(408)-589-5555' = ANY (phones);

Expand Arrays
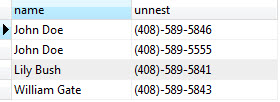
PostgreSQL provides the unnest() function to expand an array to a list of rows. For example, the following query expands all phone numbers of the phones array.
SELECT
name,
unnest(phones)
FROM
contacts;
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to work with PostgreSQL array data type and introduced you to some of the most important array operators and functions.
See more
PostgreSQL Tutorial: Data Types
PostgreSQL Documentation: Array Types

