August 4, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about the PL/pgSQL case that executes statements based on a certain condition.
Table of Contents
Introduction to PL/pgSQL case statement
Besides the if statement, PostgreSQL provides you with case statements that allow you to execute a block of code based on a condition.
The case statement selects a when section to execute from a list of when sections based on a condition.
The case statement has two forms:
- Simple
casestatement - Searched
casestatement
Notice that you should not confuse about the
casestatement and case expression. Thecaseexpression evaluates to a value while thecasestatement selects a section to execute based on condition.
1) Simple case statement
Let’s start with the syntax of the simple case statement:
case search-expression
when expression_1 [, expression_2, ...] then
when-statements
[ ... ]
[else
else-statements ]
END case;
The search-expression is an expression that evaluates to a result.
The case statement compares the result of the search-expression with the expression in each when branch using equal operator ( =) from top to bottom.
If the case statement finds a match, it will execute the corresponding when section. Also, it stops comparing the result of the search-expression with the remaining expressions.
If the case statement cannot find any match, it will execute the else section.
The else section is optional. If the result of the search-expression does not match expression in the when sections and the else section does not exist, the case statement will raise a case_not_found exception.
The following is an example of the simple case statement.
do $$
declare
rate film.rental_rate%type;
price_segment varchar(50);
begin
-- get the rental rate
select rental_rate into rate
from film
where film_id = 100;
-- assign the price segment
if found then
case rate
when 0.99 then
price_segment = 'Mass';
when 2.99 then
price_segment = 'Mainstream';
when 4.99 then
price_segment = 'High End';
else
price_segment = 'Unspecified';
end case;
raise notice '%', price_segment;
end if;
end; $$
Output:
NOTICE: High End
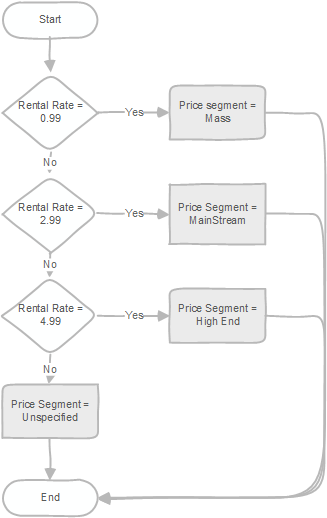
This example first selects the film with id 100. Based on the rental rate, it assigns a price segment to the film that can be mass, mainstream, or high end. In case the price is not 0.99, 2.99 or 4.99, the case statement assigns the film the price segment as unspecified.
The following flowchart illustrates the simple case statement in this example:
2) Searched case statement
The following syntax shows syntax of the searched case statement:
case
when boolean-expression-1 then
statements
[ when boolean-expression-2 then
statements
... ]
[ else
statements ]
end case;
In this syntax, the case statement evaluates the boolean expressions sequentially from top to bottom until it finds an expression that evaluates to true
Once it finds an expression that evaluates to true, the case statement executes the corresponding when section and immediately stops searching for the remaining expressions.
In case no expression evaluates to true, the case statement will execute the the else section.
The else section is optional. If you omit the else section and there is no expression evaluates to true, the case statement will raise the case_not_found exception.
The following example illustrates how to use a simple case statement:
do $$
declare
total_payment numeric;
service_level varchar(25) ;
begin
select sum(amount) into total_payment
from Payment
where customer_id = 100;
if found then
case
when total_payment > 200 then
service_level = 'Platinum' ;
when total_payment > 100 then
service_level = 'Gold' ;
else
service_level = 'Silver' ;
end case;
raise notice 'Service Level: %', service_level;
else
raise notice 'Customer not found';
end if;
end; $$
How it works:
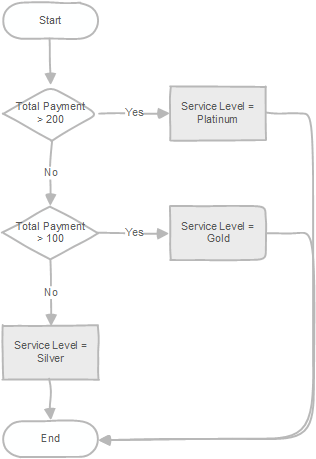
- First, select the total payment paid by the customer id 100 from the
paymenttable. - Then, assign the service level to the customer based on the total payment
The following diagram illustrates the logic:
Notice that the searched case statement is similar to the if then elsif statement.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PL/pgSQL case that execute statements based on a certain condition.

