August 3, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL INTERSECT operator to combine result sets of two or more queries.
Table of Contents
Introduction to PostgreSQL INTERSECT operator
Like the UNION and EXCEPT operators, the PostgreSQL INTERSECT operator combines result sets of two or more SELECT statements into a single result set.
The INTERSECT operator returns any rows that are available in both result sets.
The following illustration shows the final result set produced by the INTERSECT operator.

The final result set is represented by the yellow area where circle A intersects with circle B.
The following illustrates the syntax of the INTERSECT operator:
SELECT select_list
FROM A
INTERSECT
SELECT select_list
FROM B;
To use the INTERSECT operator, the columns that appear in the SELECT statements must follow the folowing rules:
- The number of columns and their order in the
SELECTclauses must be the same. - The data types of the columns must be compatible.
PostgreSQL INTERSECT with ORDER BY clause
If you want to sort the result set returned by the INTERSECT operator, you place the ORDER BY at the final query in the query list like this:
SELECT select_list
FROM A
INTERSECT
SELECT select_list
FROM B
ORDER BY sort_expression;
PostgreSQL INTERSECT operator examples
We’ll use the top_rated_films and most_popular_films tables created in the UNION tutorial:
The top_rated_films table:
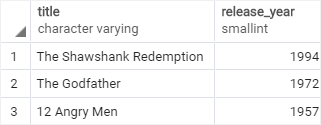
The most_popular_films table:
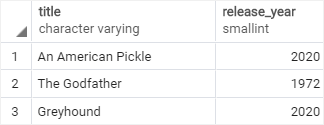
To get popular films which are also top rated films, you use the INTERSECT operator as follows:
SELECT *
FROM most_popular_films
INTERSECT
SELECT *
FROM top_rated_films;
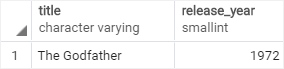
The result set returns one film that appears on both tables.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL INTERSECT operator to combine result sets returned by multiple queries.

