八月 9, 2023
摘要:在本教程中,您将会使用 JDBC 事务 API 了解 JDBC PostgreSQL 事务。
目录
在某些情况下,您不希望一条 SQL 语句生效,除非另一条 SQL 语句完成。例如,当您想要插入新演员时,您还想指定该演员参演的电影。
为了确保两个操作都生效或两个操作都不发生,您可以使用事务。
根据定义,事务是作为单个单元执行的一组语句。换句话说,要么所有语句都成功执行,要么没有一个执行。
禁用自动提交模式
当您建立与 PostgreSQL 数据库的连接时,它处于自动提交模式。这意味着每条 SQL 语句都被视为一个事务并自动提交。
如果要在事务中封装一条或多条语句,则必须禁用自动提交模式。为此,您可以按如下所示,调用Connection对象的setAutoCommit()方法:
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
最佳的实践是仅针对事务模式禁用自动提交模式。它可以让您避免为多个语句持有数据库锁。
提交事务
要提交事务,请调用 Connection 对象的 commit 方法,如下所示:
conn.commit();
当您调用commit()方法时,所有先前的语句都将作为一个单元一起提交。
回滚事务
如果一条语句的结果不是您所期望的,您可以使用Connection对象的rollback()方法来中止当前事务并将值恢复为原始值。
conn.rollback();
PostgreSQL JDBC 事务示例
让我们来看一个使用 JDBC API 执行 PostgreSQL 事务的示例。
我们将在actor表中插入一个新演员,并为该演员分配一部由电影 id 指定的电影。
首先,创建一个代表演员的类,如下所示:
package net.rockdata.tutorial;
/**
*
* @author rockdata.net
*/
public class Actor {
/**
* actor's first name
*/
private String firstName;
/**
* actor's last name
*/
private String lastName;
/**
* initialize an actor with the first name and last name
*
* @param firstName
* @param lastName
*/
public Actor(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
/**
* initialize an actor
*/
public Actor() {
}
/**
* @return the firstName
*/
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
/**
* @param firstName the firstName to set
*/
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
/**
* @return the lastName
*/
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
/**
* @param lastName the lastName to set
*/
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}
然后,创建一个用于演示的 App 类。
/**
* need to fix the db ALTER TABLE film_actor ALTER COLUMN actor_id TYPE INT;
* ALTER TABLE film_actor ALTER COLUMN film_id TYPE INT;
*/
package net.rockdata.tutorial;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
*
* @author rockdata.net
*/
public class App {
private final String url = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost/dvdrental";
private final String user = "postgres";
private final String password = "postgres";
/**
* Connect to the PostgreSQL database
*
* @return a Connection object
* @throws java.sql.SQLException
*/
public Connection connect() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
}
/**
* Close a AutoCloseable object
*
* @param closable
*/
private App close(AutoCloseable closeable) {
try {
if (closeable != null) {
closeable.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return this;
}
/**
* insert an actor and assign him to a specific film
*
* @param actor
* @param filmId
*/
public void addActorAndAssignFilm(Actor actor, int filmId) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt2 = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
// insert an actor into the actor table
String SQLInsertActor = "INSERT INTO actor(first_name,last_name) "
+ "VALUES(?,?)";
// assign actor to a film
String SQLAssignActor = "INSERT INTO film_actor(actor_id,film_id) "
+ "VALUES(?,?)";
int actorId = 0;
try {
// connect to the database
conn = connect();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// add actor
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(SQLInsertActor,
Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
pstmt.setString(1, actor.getFirstName());
pstmt.setString(2, actor.getLastName());
int affectedRows = pstmt.executeUpdate();
if (affectedRows > 0) {
// get actor id
rs = pstmt.getGeneratedKeys();
if (rs.next()) {
actorId = rs.getInt(1);
if (actorId > 0) {
pstmt2 = conn.prepareStatement(SQLAssignActor);
pstmt2.setInt(1, actorId);
pstmt2.setInt(2, filmId);
pstmt2.executeUpdate();
}
}
} else {
// rollback the transaction if the insert failed
conn.rollback();
}
// commit the transaction if everything is fine
conn.commit();
System.out.println(
String.format("The actor was inserted with id %d and "
+ "assigned to the film %d", actorId, filmId));
} catch (SQLException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
// roll back the transaction
System.out.println("Rolling back the transaction...");
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.rollback();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
} finally {
this.close(rs)
.close(pstmt)
.close(pstmt2)
.close(conn);
}
}
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
App app = new App();
// OK transaction
app.addActorAndAssignFilm(new Actor("Bruce", "Lee"), 1);
// Failed transaction
// app.addActorAndAssignFilm(new Actor("Lily", "Lee"), 9999);
}
}
App 类如何工作。
connect()方法建立与 dvdrental 数据库的连接并返回一个 Connection 对象。
close()方法用于关闭一个可关闭对象,例如 Resultset、Statement 和 Connection。
addActorAndAssignFilm()方法插入一个新演员,并在事务中将电影分配给该演员。
- 首先,将一个新演员插入 actor 表中。
- 接下来获取新插入的演员的 id。
- 然后,通过在 film_actor 表中插入新行,将演员分配给电影。
- 之后,如果步骤2和3都成功,则提交事务。否则,回滚事务。
- 最后,关闭 ResultSet、PreparedStatement 和 Connection 对象。
如果我们执行第一个场景的程序,我们会得到以下结果:
run:
The actor was inserted with id 217 and assigned to the film 1
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 2 seconds)
我们可以通过查询actor表来验证:
SELECT
actor_id,
first_name,
last_name
FROM
actor
ORDER BY
actor_id DESC;
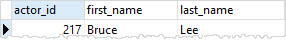
还有film_actor表:
SELECT
actor_id,
film_id
FROM
film_actor
WHERE
actor_id = 217;

现在,如果我们插入一个新演员并将她分配给一部不存在的电影,则会出现以下错误消息:
run:
ERROR: insert or update on table "film_actor" violates foreign key constraint "film_actor_film_id_fkey"
Detail: Key (film_id)=(9999) is not present in table "film".
Rolling back the transaction...
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
事务被回滚,并且没有任何内容被插入到actor和film_actor表中。
在本教程中,您学习了如何使用 JDBC 事务 API 执行事务,以确保 PostgreSQL 数据库中数据的完整性。

