September 19, 2023
Summary: The PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() function splits a string on a specified delimiter and returns the nth substring.
Table of Contents
Syntax
The following illustrates the syntax of the PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() function:
SPLIT_PART(string, delimiter, position)
Arguments
The SPLIT_PART() function requires three arguments:
1) string
is the string to be split.
2) delimiter
The delimiter is a string used as the delimiter for splitting.
3) position
is the position of the part to return, starting from 1. The position must be a positive integer.
If the position is greater than the number of parts after splitting, the SPLIT_PART() function returns an empty string.
Return Value
The SPLIT_PART() function returns a part as a string at a specified position.
Examples
See the following statement:
SELECT SPLIT_PART('A,B,C', ',', 2);
The string 'A,B,C' is split on the comma delimiter (,) that results in 3 substrings: ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’.
Because the position is 2, the function returns the 2nd substring which is ‘B’.
Here is the output:

See the following payment table in the sample database.

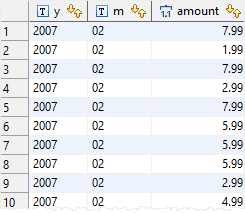
The following statement uses the SPLIT_PART() function to return the year and month of the payment date:
SELECT
split_part(payment_date::TEXT,'-', 1) y,
split_part(payment_date::TEXT,'-', 2) m,
amount
FROM
payment;
The output is:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() function to get part of a string at a specified position after splitting.
See more
PostgreSQL Tutorial: String Functions
PostgreSQL Documentation: String Functions and Operators

