August 3, 2023
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN clause to select data from multiple tables.
Table of Contents
Introduction to PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN clause
Suppose that you have two tables: A and B.
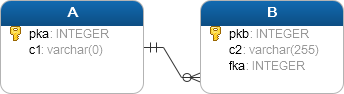
Each row in the table A may have zero or many corresponding rows in the table B while each row in the table B has one and only one corresponding row in the table A .
To select data from the table A that may or may not have corresponding rows in the table B , you use the LEFT JOIN clause.
The following statement illustrates the LEFT JOIN syntax that joins the table A with the table B :
SELECT
pka,
c1,
pkb,
c2
FROM
A
LEFT JOIN B ON pka = fka;
To join the table A with the table B table using a left join, you follow these steps:
- First, specify the columns in both tables from which you want to select data in the
SELECTclause. - Second, specify the left table (table
A) in theFROMclause. - Third, specify the right table (table
B) in theLEFT JOINclause and the join condition after theONkeyword.
The LEFT JOIN clause starts selecting data from the left table. For each row in the left table, it compares the value in the pka column with the value of each row in the fka column in the right table.
If these values are equal, the left join clause creates a new row that contains columns that appear in the SELECT clause and adds this row to the result set.
In case these values are not equal, the left join clause also creates a new row that contains columns that appear in the SELECT clause. In addition, it fills the columns that come from the right table with NULL.
The following Venn diagram illustrates how the LEFT JOIN clause works:
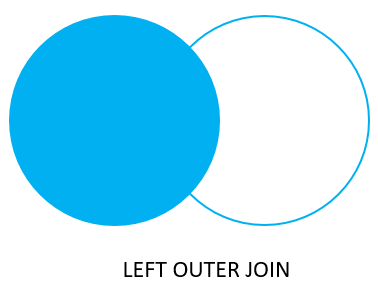
Note that the LEFT JOIN is also referred to as LEFT OUTER JOIN.
PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN examples
Let’s look at the following film and inventory tables from the sample database.
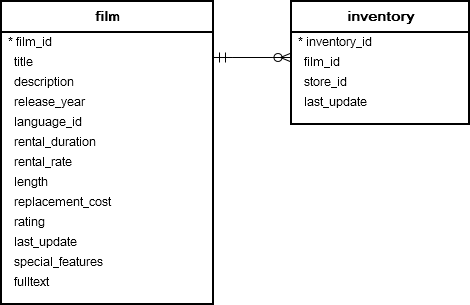
Each row in the film table may have zero or many rows in the inventorytable. Each row in the inventory table has one and only one row in the film table.
The film_id column establishes the link between the film and inventory tables.
The following statement uses the LEFT JOIN clause to join film table with the inventorytable:
SELECT
film.film_id,
title,
inventory_id
FROM
film
LEFT JOIN inventory
ON inventory.film_id = film.film_id
ORDER BY title;

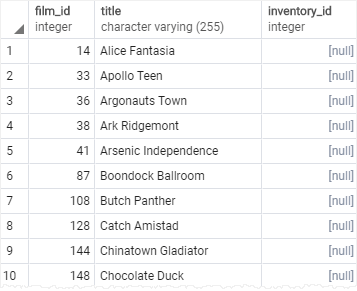
When a row from the film table does not have a matching row in the inventorytable, the value of the inventory_id column of this row is NULL.
The following statement adds a WHERE clause to find the films that are not in the inventory:
SELECT
film.film_id,
film.title,
inventory_id
FROM
film
LEFT JOIN inventory
ON inventory.film_id = film.film_id
WHERE inventory.film_id IS NULL
ORDER BY title;
The following statement returns the same result. The difference is that it uses the table aliases to make the query more concise:
SELECT
f.film_id,
title,
inventory_id
FROM
film f
LEFT JOIN inventory i
ON i.film_id = f.film_id
WHERE i.film_id IS NULL
ORDER BY title;
If both tables have the same column name used in the ON clause, you can use the USING syntax like this:
SELECT
f.film_id,
title,
inventory_id
FROM
film f
LEFT JOIN inventory i USING (film_id)
WHERE i.film_id IS NULL
ORDER BY title;
This technique is useful when you want to select rows from one table that do not have matching rows in another table.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN clause to select rows from one table that may or may not have corresponding rows in other tables.

