August 2, 2023
Summary: In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint to create the PostgreSQL identity column for a table.
Table of Contents
Introduction to PostgreSQL identity column
PostgreSQL version 10 introduced a new constraint GENERATED AS IDENTITY that allows you to automatically assign a unique number to a column.
The GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint is the SQL standard-conforming variant of the good old SERIAL column.
The following illustrates the syntax of the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint:
column_name type GENERATED { ALWAYS | BY DEFAULT } AS IDENTITY[ ( sequence_option ) ]
In this syntax:
- The type can be
SMALLINT,INT, orBIGINT. - The
GENERATED ALWAYSinstructs PostgreSQL to always generate a value for the identity column. If you attempt to insert (or update) values into theGENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITYcolumn, PostgreSQL will issue an error. - The
GENERATED BY DEFAULTalso instructs PostgreSQL to generate a value for the identity column. However, if you supply a value for insert or update, PostgreSQL will use that value to insert into the identity column instead of using the system-generated value.
PostgreSQL allows you a table to have more than one identity column. Like the SERIAL, the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint also uses the SEQUENCE object internally.
PostgreSQL identity column examples
A) GENERATED ALWAYS example
First, create a table named color with the color_id as the identity column:
CREATE TABLE color (
color_id INT GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
color_name VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
Second, insert a new row into the color table:
INSERT INTO color(color_name)
VALUES ('Red');
Because color_id column has the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint, PostgreSQL generates a value for it as shown in the query below:
SELECT * FROM color;

Third, insert a new row by supplying values for both color_id and color_name columns:
INSERT INTO color (color_id, color_name)
VALUES (2, 'Green');
PostgreSQL issued the following error:
ERROR: cannot insert into column "color_id"
DETAIL: Column "color_id" is an identity column defined as GENERATED ALWAYS.
HINT: Use OVERRIDING SYSTEM VALUE to override.
To fix the error, you can use the OVERRIDING SYSTEM VALUE clause as follows:
INSERT INTO color (color_id, color_name)
OVERRIDING SYSTEM VALUE
VALUES(2, 'Green');
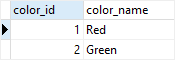
Or use GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY instead.
B) GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY example
First, drop the color table and recreate it. This time we use the GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY instead:
DROP TABLE color;
CREATE TABLE color (
color_id INT GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,
color_name VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
Second, insert a row into the color table:
INSERT INTO color (color_name)
VALUES ('White');
It works as expected.
Third, insert another row with a value for the color_id column:
INSERT INTO color (color_id, color_name)
VALUES (2, 'Yellow');
Unlike the previous example that uses the GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY constraint, the statement above works perfectly fine.
C) Sequence options example
Because the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint uses the SEQUENCE object, you can specify the sequence options for the system-generated values.
For example, you can specify the starting value and the increment as follows:
DROP TABLE color;
CREATE TABLE color (
color_id INT GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY
(START WITH 10 INCREMENT BY 10),
color_name VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
In this example, the system-generated value for the color_id column starts with 10 and the increment value is also 10.
First, insert a new row into the color table:
INSERT INTO color (color_name)
VALUES ('Orange');
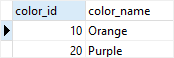
The starting value for color_id column is ten as shown below:
SELECT * FROM color;

Second, insert another row into the color table:
INSERT INTO color (color_name)
VALUES ('Purple');
The value for the color_id of the second row is 20 because of the increment option.
SELECT * FROM color;
Adding an identity column to an existing table
You can add identity columns to an existing table by using the following form of the ALTER TABLE statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ALTER COLUMN column_name
ADD GENERATED { ALWAYS | BY DEFAULT } AS IDENTITY { ( sequence_option ) }
Let’s see the following example.
First, create a new table named shape:
CREATE TABLE shape (
shape_id INT NOT NULL,
shape_name VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
Second, change the shape_id column to the identity column:
ALTER TABLE shape
ALTER COLUMN shape_id ADD GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY;
Note that the shape_id needs to have the NOT NULL constraint so that it can be changed to an identity column. Otherwise, you’ll get an error as follows:
ERROR: column "shape_id" of relation "shape" must be declared NOT NULL before identity can be added
SQL state: 55000
The following command describes the shape table in psql tool:
\d shape
It returns the following output which is what we expected:
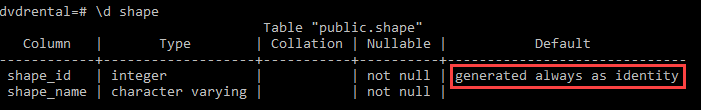
Changing an identity column
You can change the characteristics of an existing identity column by using the following ALTER TABLE statement:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ALTER COLUMN column_name
{ SET GENERATED { ALWAYS| BY DEFAULT } |
SET sequence_option | RESTART [ [ WITH ] restart ] }
For example, the following statement changes the shape_id column of the shape table to GENERATED BY DEFAULT:
ALTER TABLE shape
ALTER COLUMN shape_id SET GENERATED BY DEFAULT;
The following command describes the structure of the shape table in the psql tool:
\d shape
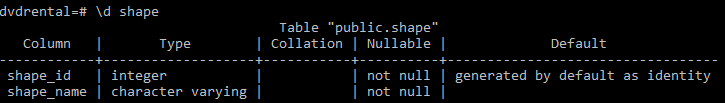
As you can see from the output, the shape_id column changed from GENERATED ALWAYS to GENERATED BY DEFAULT.
Removing the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint
The following statement removes the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint from an existing table:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ALTER COLUMN column_name
DROP IDENTITY [ IF EXISTS ]
For example, you can remove the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint column from the shape_id column of the shape table as follows:
ALTER TABLE shape
ALTER COLUMN shape_id
DROP IDENTITY IF EXISTS;
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL identity column and how to manage it by using the GENERATED AS IDENTITY constraint.

